Kilimanjaro: Undergoing Severe Exertion
“The mere animal pleasure of travelling in a wild unexplored country is very great. When one lands of a couple of thousand feet elevation, brisk exercise imparts elasticity to the muscles, fresh and healthy blood circulates through the brain, the mind works well, the eye is clear, the step is firm … the mind is made more self-reliant… No one can truly experience the charm of repose unless he has undergone severe exertion.” —Dr. David Livingstone
I don’t know about the mind working so well at high elevation, as mine seemed to work a bit against me just before the summit, of Kilimanjaro, but I do know about the charm of repose, as I am writing this from the exotic island of Zanzibar, a place Livingstone knew well. This is where he ordered supplies and hired porters for his trips to the interior of the “Dark Continent,” so called because on maps it was largely unexplored. I thought about Livingstone’s biblical sufferings while I tried, for the third time, to summit Kilimanjaro, all to raise money for Save One Life. I did summit twice before, in 2011 and in 2016. But this time seemed at once easier—been there, done that—and harder—that much older, and lacking the prep time needed.
Want to know what it was all like? Read on!
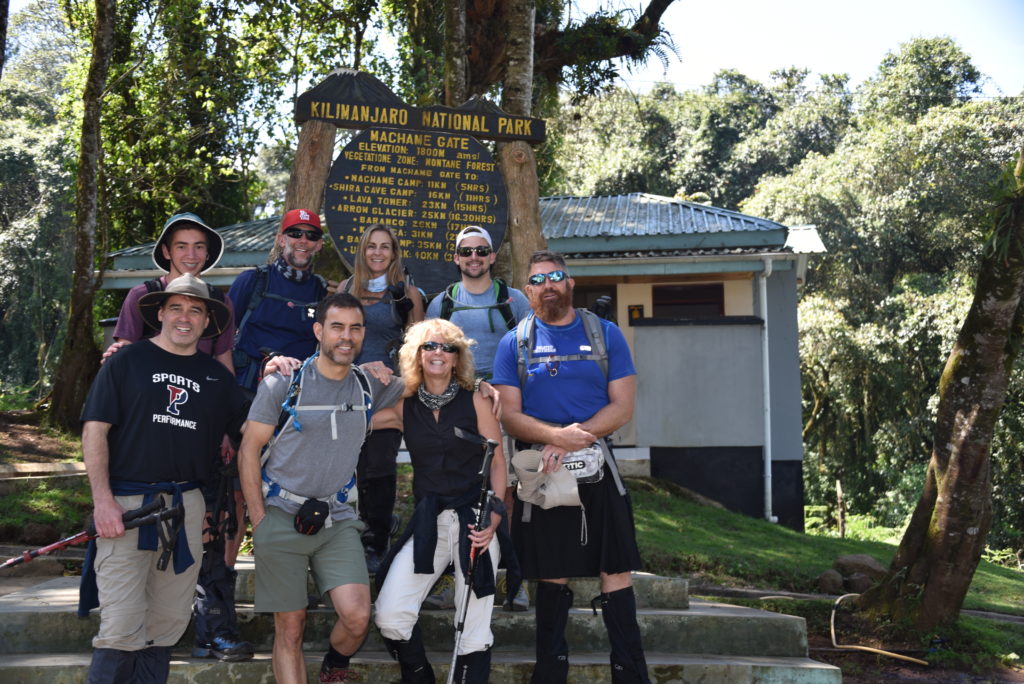

Monday August 5, 2019 DAY 1
Day 1 on the mountain is done! I’m lying in a dusty tent, snug in my 0° sleeping bag, everything organized and ready for tomorrow’s hike. My sleeping bag is an engineering marvel. It compresses down to a small package but traps heat so well that even in 0° weather you can sleep pretty much naked and not feel cold. I did the entire 4.5 hour climb today with no problem. I wasn’t wearing my pack this time and felt like I was cheating… but it was a good call. I had a two-month, off and on back spasm this spring, which finally resolved but not in enough time to really get strong for the climb. A knee injury May 6 forfeited all my running, which would have helped aerobically.
We had a long drive to Arusha, Tanzania, from Nairobi, Kenya. We were all up and ready by 7:30 am. The drive took about 8 hours by bus, which we thought might be easier than flying; I flew last time and some of our luggage didn’t make it in time for the climb. It’s just a bit nerve wracking! The bus was easier, and we saw the countryside, and made new friends! A group of Polish people hopped on too, and one of the guys, Michael, was quite the clown! Wiry with crazy blue eyes, he kept us laughing… and he was drinking something from his “water” bottle! In fact, we would see him and his team on the climb, and we were pretty sure he was drinking each night into the climb, which is insane!
Once we got through customs at the border of Kenya and Tanzania, we enjoyed the Tanzanian countryside. What a change from Kenya! There is a drought, and the landscape became dry, dusty, stripped. Dust devils swirled madly in anger on either side of our highway. My teammates were giddy with excitement; our trip was really starting.
We finally arrived at a place I know well—Kibo Palace hotel in Arusha. I really like Arusha—a small city at the foothills of Mount Meru and Kilimanjaro. We quickly checked in. Then the guides arrived: Jackson Tsui, a tall Tanzanian with a soft voice, and Edwin! I had Edwin as a guide three years ago! And Jacob Slaa, who climbed with me in 2011. What are the odds?

Back at my hotel room, we had to pack for a 6-day climb; I finished my blog and saw that I hit my fundraising goal: $10,000! This helped me have a wonderful night’s sleep before the climb started.
Our team? Wendie and Ric Chadd from California. Wendie and I have known one another for 20 years. She and Ric have a son with hemophilia, and Wendie works for specialty pharmacy NuFactor, owned by FFF Enterprises, whose CEO and founder, Patrick Schmidt, is a longtime friend and supporter of Save One Life. Mike Adelman: senior vice president of Aptevo, which makes Xinity. He climbed and summited with me in 2016. His friend Jim Palmer, and son Sam (age 14). Jim is surgeon from Philadelphia—friendly and positive. He also summited with me in 2016—lots of suffering on the way down on that trip! Myles Ganley, person with hemophilia B, age 25. Strong and fit! Shannon Peterkin, ex-Navy from Louisiana, big as a mountain himself. His red hair and prominent beard led the guides to nickname him “Simba,” which means lion.

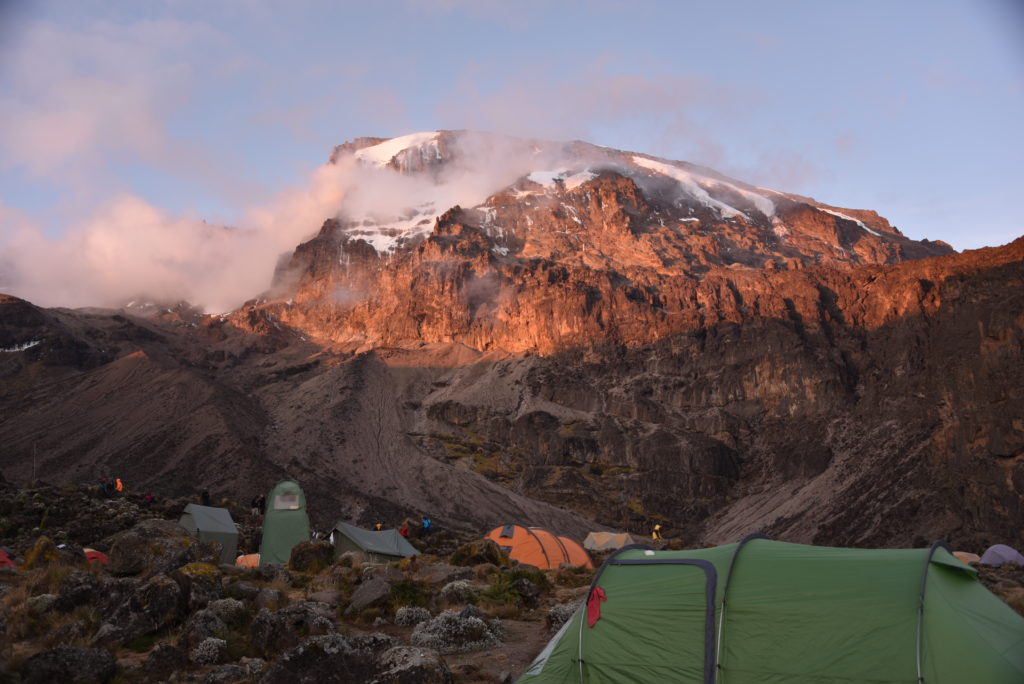
We took a two-hour bus ride to the Machame Gate (5,718 ft), and waited for paperwork to be done, and for other groups to set off. Then through the gate and off we went! Through the rainforest we trekked, gaining altitude. The forest is thick and primeval, with trees and vines covered in green velvet. The air was thick and moist with growth and rot. We needed to go pole, pole (slow, slow), and Edwin set the pace. Jbiri was the young porter who carried my pack, which was light anyway. Mike and I were the first to stroll into camp, at Machame (9,927 ft). We signed in, then Edwin took us to our camp.
We didn’t eat till 8:30 pm but everyone was laughing and joking. The 30 porters carry everything we need for 6 days. Tonight we had fried tilapia, fries and spinach. Outside, the stars were shining bright. You could see the Milky Way streaking across the sky like a diaphanous scarf.
Tuesday August 5, 2019 DAY 2
It’s chilly! We were all awake at 5 am, from the rustling and chatting of the porters in the frosty air as they packed up camp. We awake with hot tea in our sleeping bags, brought each morning by two of the porters, who carefully add sugar and milk, or whatever you like. A hot bowl of water follows, and since you cannot shower for 6 days, this little bowls becomes a very precious commodity! You quickly learn to appreciate the simple things. Breakfast was omelets, fruit, toast, and oatmeal. Jim and Sam look tired this morning, and are not feeling well. So early in the trip, this does not bode well.
We started hiking after camp broke, and did the half day climb up, and up to Shira Cave Camp. Single file, taking huge steps, at least at a 45° angle, if not steeper. This was one of my favorite parts of the climb. It’s like climbing Mt. Washington for 5 straight hours. Rocks everywhere! Sometimes the ground was a single molten lava rock, lumpy but smooth. We saw our first senecios, funny-looking trees related to the daisies.

Our quads got quite the wake-up workout today! We arrived at Shira Cave Camp (12,355 ft) around 3 pm. Jim looked very wan. Sam was feeling better. I was with Jim in 2016, and he was strong right till summit night, so this was not right for him. Eventually Jim decided not to go forward; he and Sam packed up and with one guide, Prosper, and two porters, they left.
We would miss him; his smile and positive attitude really helps everyone in a group that eventually would suffer. But all went to our tents and I slept from 9:20 pm till 5 am again. I felt fantastic, totally enjoying everything. But now Shannon wasn’t feeling well.
Wednesday August 7, 2019 DAY 3
We awoke to another chilly morning. But we could see our goal, Kibo summit, in the background! We had oatmeal, eggs, pancakes, toast and jam for breakfast. We were off by 8 am, to Barranco camp, which would take us 8 hours. Within 30 minutes we were warm and began discarding jackets. I forgot the path went upwards so much, through scruffy little hills, and huge boulders, spewed out of the volcano probably a million years ago!
The view was spectacular, the sky blue. We were looking down at a solid cloud cover, like cotton balls forming a welcome mat. And to the west, Shira Mountain and Meru popped up through the cotton, and to the East, Kibo, summit of Kilimanjaro. Situated near the fault-line of two tectonic plates, Kilimanjaro began to build itself up around 750,000 years ago, via thousands of years of lava explosions from the volcanic cones of Shira, Mawenzi, and Kibo.
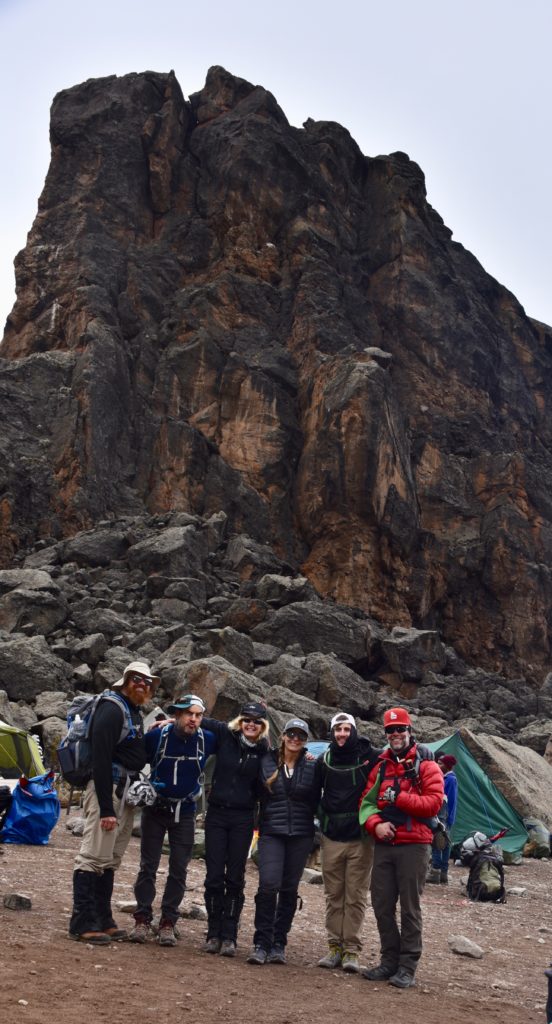

Shannon didn’t eat at all as the day went on, and we determined this was a bad combination of Diamox (altitude medicine) and malaria meds (which he didn’t need). Perhaps this is what Jim suffered from too?
I felt great, strong and focused. Lots and lots of hiking, and all good. We all seemed to need to pee every hour—a side effect of the Diamox. It got so ridiculous that we were all losing our modesty quickly.
We stopped at the 300-foot Lava Tower, all in good spirits but
starting to feel the altitude at about 15,000 feet now. Lava
Tower is a “volcanic plug”; at some point long ago, lava spewed out of a vent
at the base of where Lava Tower now stands, cooled, and hardened, thus stopping
up the vent beneath.
We had another nice lunch, then packed up and headed down into the Barranco Valley. As I predicted, it was chilly, temps dropping as we lowered ourselves down the rocky hillside and into the barren valley. I also love this part of the hike! Maybe just because I know this so well. But here we saw the towering senecios and other strange looking plants, like something from a Dr. Seuss story, the Lorax, or from one of the movies where people go back in time to the dinosaur age. We seemed to shrink as the trees towered over us. Ric and Wendie loved it. We finally arrived at camp (Barranco, 13,066 ft), and saw the intimidating 800-foot Barranco wall, which we would climb in the morning. So, we climbed up to 15,000 ft then climbed down, to acclimatize. Dinner and bed early!
Thursday August 8, 2019 DAY 4
This was the day! This very night we would begin our summit push. But first, we had to get out of the Barranco valley. Again, we are awoken each morning in our dusty, cold tents, by two young porters who quietly and gently bring us tea, coffee or hot chocolate, even as they are bundled up and facing the cold. They gently and respectfully pour the hot water, dip in the tea bag, stir in the sugar, until it’s just right. Then they zip up the tent when they leave; I feel spoiled. I get to have hot tea with cream and sugar while still in my sleeping bag. Even though we have gone without showers for 4 days, and are covered in dust, we feel like royalty having hot drinks in a tent!
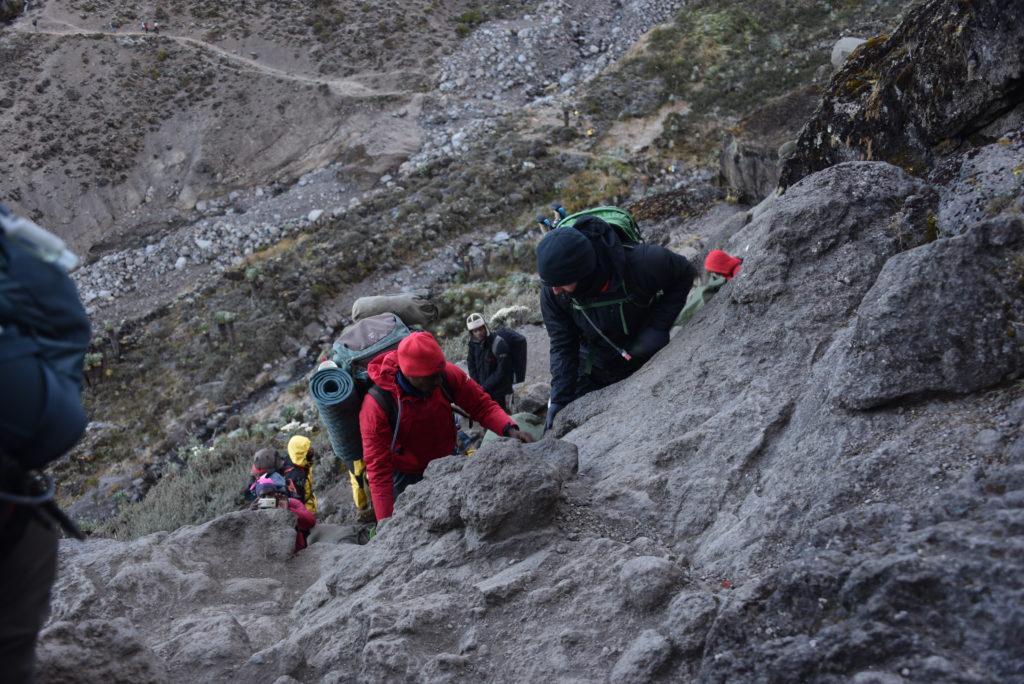
We are pumped at breakfast. Shannon is feeling better, now that he has stopped taking malaria pills. He makes an amazing recovery and starts eating again. Jackson wants to be one of the first out, so we start out around 7 am. Straight up the Barranco wall, until we are about an hour later doing a “scramble,” hand to foot. The guides are there to help us. We have to navigate “kissing rock,” so named because you have to hug it in order to slide around it. A bit hairy! We each look back every 20 minutes or so, and the camp we just left gets smaller and smaller. Mike cracks a joke about the strange yellow tents that are all connected, like gerbil tunnels. They haven’t started to break camp yet. I joke back that maybe they can’t find their way out?
I’m not using poles but just powering up with my quads, feeling excellent.
Everyone is doing great. Before long we reach the top, and the view is glorious! To our left, the east, with the sun starting to shine above the clouds (we are above the clouds!), and below us, colorful dots that are the tents that made up our camp. We pause for water, and photos. And always, a bathroom break.
Then we start the hike down, which takes the rest of the morning and into the afternoon. It’s a long slog, down from the wall, had to foot, carefully, down sidewinding rocky paths, and finally onto long stretches of dusty trails. We would hike about 7-8 hours this day, all the way to Barafu Camp (15,239 ft). Still, I felt good, solid. Shannon was recovered, everyone was doing well. We reached the camp, and our tents were already pitched. It’s very rocky here, chilly, but nice when the sun is out.

Soon we had our dinner, around 5, and straight to bed, after sorting everything out gear wise. I fell right asleep for 4 hours. In fact, I got the best sleep and felt great. So what happened that night to me?
We put on our gear at 11 pm, getting ready for a 12 am departure. Base layer of wool; fleece pants and top. Puffy coat. Rain pants over fleece, and my EMS tough jacket that goes everywhere with me. One iPod was dead, but the other seemed to have full juice. I was feeling so good I didn’t feel the need for it! Water, gloves, hat, and we were ready to go. Off into the chilled night air; I figured it got to about 20°, which isn’t bad at all, and later when the wind came, about 10-15°.
It was all good.
I felt strong with no digestive issues at all, this whole trip, and had a full stomach of pasta. From 12 am-5 am I felt great. The summit push is all short switchbacks, one foot plodding after the other. Things could not have been better. At 5 am we took a break, and Ric, sitting on a rock, looked crushed. He asked Mike for some motivation. I gave him some: You can do it! You’ve come this far! It’s only about an hour! He rallied and pushed on. Jacob had given me Red Bull around 3 am, freezing cold and tasting bitter, but I guzzled it, knowing from experience it can really help. I don’t recall ever feeling bad or sore. Just a bit tired, as the legs slowed.

I looked up from time to time to see the stunning white stars in the black heavens. I thought: They are beautiful, but cold and unfeeling. They have no pity. Not like our guides: they were great. Warm, caring, always there to help. Team Kilimanjaro! My favorite moment was when Myles reached down to give me a hand up. Myles, the youngest, and with hemophilia, was crushing this mountain! He made it look easy. The stars stood back with a cold, clinical eye to all our suffering. It was harder to breathe as we went on.
Wisely, Jackson put Ric first. I recall when Jonas did that to me in 2011; I was flagging so bad, and thought, Oh no, I will slow down the pack! But just the opposite: I picked up steam! But come 6 am- 7 am, I was definitely slowing. The sun came up below us, lighting the clouds pink from underneath. My feet: it started as forward stumbles, like I had stepped on wobbly stones. I tricked myself into believing I had just tripped on some rocks.

Then side to side stumbles, like I was drunk. I kept apologizing to Jacob, as I thought I was not paying attention. My mind seemed sharp and my core was warm, and I was not ill; what was wrong? I had never overall felt better on Kili. But little by little, it felt like every little stabilizer muscle in my feet and ankles were giving away, like the snapping of suspensions on a bridge. I kept stopping, trying to get O2 to my feet and muscles. On KIli, at this point, oxygen was about 50% of sea level. Like trying to do spin class while breathing through a straw, someone told me.
Pretty soon, my legs were just collapsing, and once I even held onto a big rock, just to stay upright. And Stella Point (18,848 ft) was a mere 65 feet away, but straight up, the steepest part of the entire climb. How could I possibly reach that? Our team pulled further and further away, and my feet grew more and more useless. Jacob was determined to get me up there.
This became a battle between my rational brain, my legs, my willpower. All screaming at me at 18,000 feet.
I think I knew too much. This was my third climb up Kilimanjaro. The first summit was in a blinding snowstorm with -5°. Jonas dragged me up. The second summit I did with relative ease. Listening to Metallica on my iPod, encouraging another climber, dancing with the porters, I did fine. But I bonked big time on the 3-hour descent, and my legs just dissolved into gelatin. I was thinking of that while hugging the rock. How will I ever get down? It will take me another 1.5 hours at least to summit and then I have 3 hours down… It seemed impossible. You can’t climb if your legs don’t move and I could not will them to move.
Of course, I could have done it. I did it the first time and second, under worse circumstances. Now, the weather was excellent, and I was fit. But I wondered if having a back spasm for two months off and on, and then an injured knee for two months helped ruin my workouts.
And psychologically, I thought, Been there done that. I’ve summited, I have nothing left to prove! But it still eats at me, even as I write this.
So Jacob and I headed down; within 30 minutes I was getting more O2 to my legs, and was able to walk well. That’s all it took! We got back to Baranfu at 10 am, and I knew my teammates were just starting their descent. I cleaned up, ate some breakfast, tried to sleep (no way), and just waited for everyone. They appeared around noon; Shannon was exhausted! Ric and Wendie went right to sleep.
I felt cruel but I had to wake everyone up at 2 pm, so we could head out. Shannon was so tired, and Jackson made the good call to not descend to Mweka Camp (10,204 ft), which would require a 5 hour hike! Could you imagine? 7 hours of hiking, followed by an 8-9 hour summit hike straight up, three hours down, then another 5 hours, all on about 4 hours of sleep? It was only 2 hours to high camp. And it was a lovely walk down; we finally got to groomed trails, the valley to our left, lush and green. So different than the dusty, barren plateaus we were on! The sun was up, it was warm again… the night seemed a distant thought.
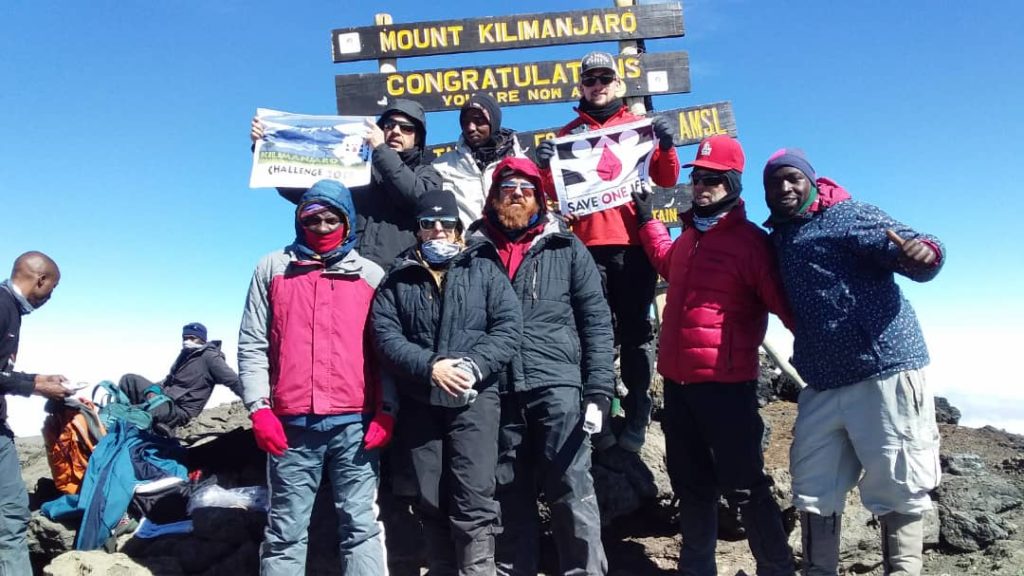

Why did I quit so close to the summit? Knowing too much, having summited before, and not enough aerobic practice? I don’t know. I wish I hadn’t quit, but I did. But I was so glad out team summited, and I was proud of them!
Saturday August 11, 3019 Mweka Gate (5,423 ft)
We were all in great spirits when we arose in the chilly air, which quickly gave away to spring like temps. Behind us, we could see Kilimanjaro startled awake with sunshine pouring into its glacier-eyes. We had a hearty breakfast while the porters broke down camp. Everyone wants to get home now! When the porters gathered around in a circle, this as the customary sign that they would perform some dancing and singing, and we would hand out tips. Edwin led the spirited songs, with a couple of the guys really getting into it! One by one, Mike handed out tips to me, and I shook hands with each and passed their $40 on. And we packed up and left! This was all downhill, and the way was muddy and slippery. I again slipped and fell into the mud, just like I did in 2016! Colobus monkeys chattered above, and the way was surrounded by lush trees, moss and fertile forests.

It took about three hours. So, we ended another trip by meeting up at the Mweka Gate, me by myself, finding Myles, Mike and Shannon together. Ric and Wendie were behind. We washed off our boots for $1, signed out of the park, and had a Coke! It was delicious! Not water from my now-stale Camelback. Even though I didn’t summit, I still shared in the celebration, and Jacob even gave me Stella Point on my certificate.
Finally Ric and Wendie showed up. Now we all had a cold beer (Coke for me), and we joked and compared notes. All in all, a great team, great comraderie. And maybe it was meant to be? I already started thinking about a return trip, and Jackson had me thinking of going up the seven-day Rongai instead.
And when I later checked Facebook, saying that I had quit so close to the summit, everyone chastised me kindly: I did not quit, I did great… 65+ comments and more coming. Best of all? We raised a lot of money for Save One Life’s programs and families in need. And when I jokingly said I need to come back to Kili and redeem myself—who wants to come? I was only joking.
But three people already want to sign up. Make it four—count me in. See you again, Kilimanjaro!
Team, Kilimanjaro is the outfitter I have used three times now, and they are superb! I highly recommend them and will use the, again. Thanks to our guides, Jackson, Edwin, Jacob and Prosper, our cook, and all the porters! And my wonderful teammates: Wendie and Ric, Myles, Shannon, Mike, Jim and Sam. And to everyone who donated to support Save One Life!